Understanding the difference between Analog and Digital Signals
In this blog post, we’ll explore the fundamental differences between digital and analog signals, their characteristics, and applications.
Understanding the Basics:
Analog Signals:
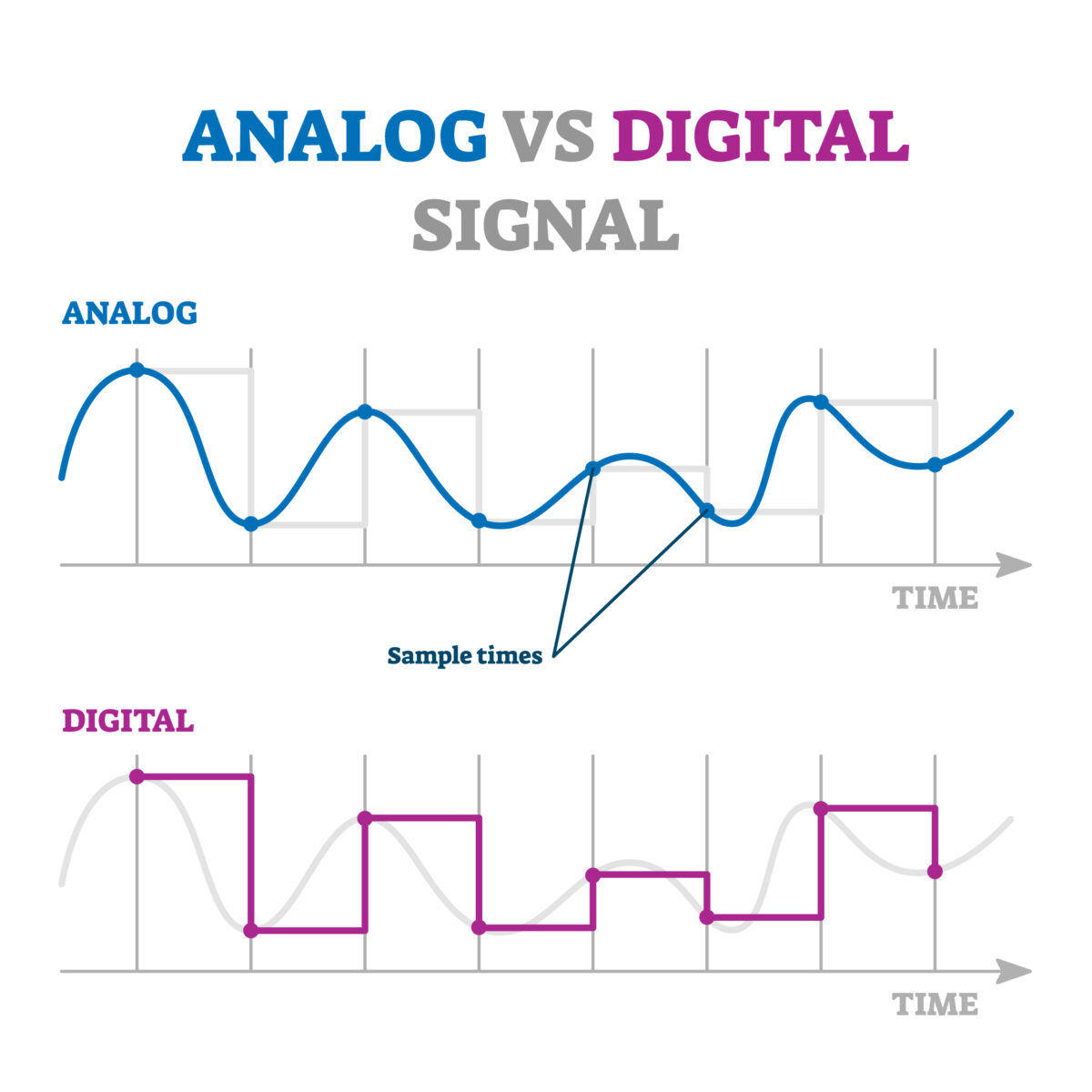
Analog signals are characterized by their continuous, smoothly varying nature. They can take an infinite number of values within a specified range.
In practical terms, analog signals are like waves, representing information such as pressure and temperature in a continuous and nuanced manner.
Digital Signals:
Digital signals, on the other hand, are discrete and comprised of specific, distinct values, typically represented in binary code (0s and 1s).
Unlike analog signals, which have a smooth curve, digital signals convey information through a series of steps or levels, allowing for precise representation and transmission of data.
Applications:
Analog signals offer a continuous and potentially precise representation of data. They are ideal for representing variables that are consistently changing. Temperature and pressure transmitters are ideally suited for analog signals as these variables change constantly. For example, a slight change in temperature can call for more heat or cooling to be applied to process.
Digital signals, being discrete, provide superior accuracy and precision, minimizing errors during data transmission. They are ideal for representing variables whose value is either one or the other. For example, a High-Level switch is best represented with a digital signal as operators will only want equipment to shut down if the fluid level has reached the high-level point or not.
Signal Integrity and Noise Immunity:
Analog signals are susceptible to noise interference, which can lead to signal distortions.
Digital signals exhibit greater resilience to noise, ensuring data integrity—particularly beneficial in environments prone to electromagnetic interference.
Integration with Automation Systems:
Analog signals are more prevalent in older automation systems, while digital signals are favored in modern setups due to their compatibility with advanced technologies.
Digital signals seamlessly integrate with automation systems, offering enhanced control, monitoring, and data analysis capabilities.
Cost and Complexity:
Analog systems tend to be simpler and more cost-effective to implement.
Digital systems may involve a higher initial investment but offer advanced features, ease of maintenance, and long-term benefits.
Conclusion:
Analog signals provide continuous and potentially cost-effective solutions, while digital signals offer precision, resilience to noise, and compatibility with modern automation systems.
For more information about your automation & control system, please contact us: