How To Safeguard & Maintain Control Panels In The Summer Heat
August 26, 2022
Electric Motor Control
November 29, 2022Winter Preparation; Electrical Heat Trace
It’s the time of year where facility managers and maintenance teams need to start thinking about preparing their process facilities for winter.
Heat tracing your process lines is a critical part of proper winter preparation. When installed and operating properly, electrical heat trace is extremely effective in preventing freezing and helping to avoid problems up and downstream of the potential freeze point.
Although the cable itself is what radiates the heat, a fully functional heat trace system is comprised of many different elements including:
Transformer – May be required to convert the supply voltage available at site to the proper voltage that the heat trace system is designed and rated for
Power Distribution Panels – A control cabinet where heat trace circuits are terminated and thermally protected by a circuit breaker. This cabinet provides technicians a convenient spot to work on the terminations as well as provides protection to the components from environmental factors like weather and machinery. Most importantly, it protects personnel from accidentally touching the electric circuits.
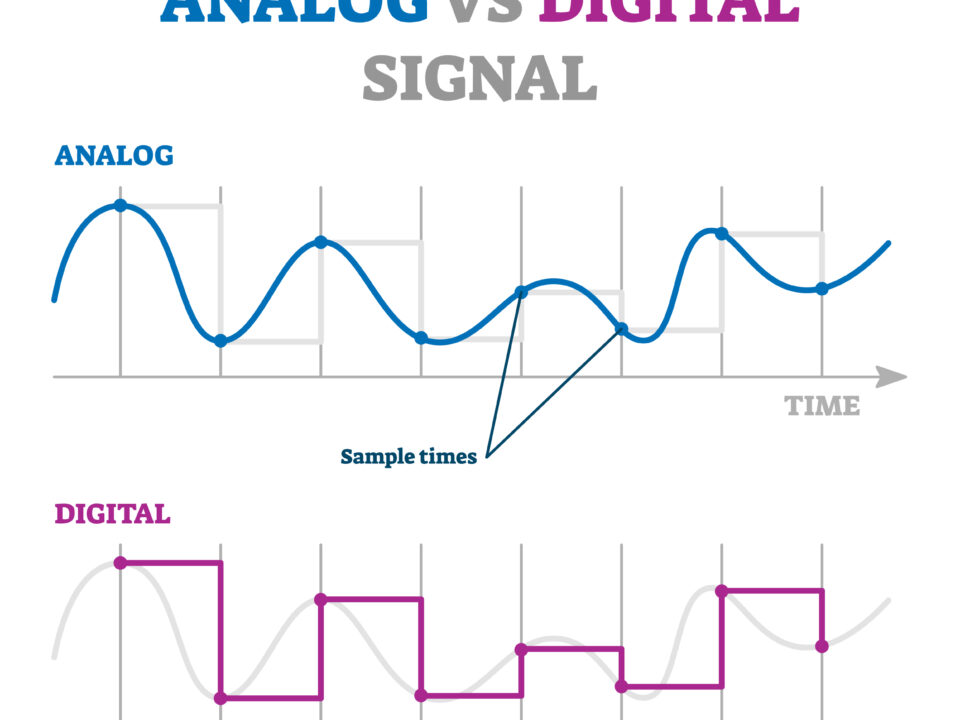
Control and Monitoring Hardware and Software – Some systems are controlled by a simple thermostat while others are controlled by advanced digital controllers which allow operators to program when and why the heat trace system turns on and off
Power connections – Varying slightly in configuration, the purpose is the same with all power connection kits; to connect incoming power to the heat trace circuit(s). Different configurations include a single connection point, multiple connections, tee’s and more
Heating cables – There are many different types of heat trace cable including (but not limited to):
Self Regulating Cable – this cable is designed to change the heat output in response to the conditions along the entire circuit. If heat loss increases, the heat output increases and vice versa
Constant Watt Heat Cable – this cable provides constant and consistent heat regardless of the conditions along the circuit
Mineral Insulated Cable – also known as “MI Cable” this is used for very high temperature and wattage applications where thermoplastic insulated cables would melt. The jacket is comprised of heat resistive materials that can withstand extremely high temperatures
Hazardous Rated Cable – used in areas where hazardous gases and materials are present
End Terminations Seals – kits that are designed to terminate the end of the circuit. Options are available to have lighted-end kits which allow operators to verify that heat trace circuits are intact just by checking that the light is on
Insulation – insulation is applied on top of heat trace cable to help reduce heat loss and is a critical component of an effective heat trace system
Megger Tests
While installing heat trace, your electrician should be performing multiple cable-insulation resistance tests to ensure the cable has not been compromised during installation. This is also known as “Meggering”. Appropriate intervals to perform megger tests include:
- Prior to installing the cable
- Before & after installing components
- Before & after insulating heat trace cable
- Prior to commissioning
Please call Crossroad Energy Solutions for help with installing or troubleshooting your electric heat trace systems:
Crossroad Energy Service Locations: Edmonton, AB
Calgary, AB
Medicine Hat, AB
Sylvan Lake, AB
Drayton Valley, AB
Claresholm, AB
Slave Lake, AB
Shaunavon, Sask
Williston, North Dakota
Sidney, Montana
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma
San Antonio, Texas
Dallas, Texas
Synder, Texas
McAllen, Texas